IOT(INTERNET OF THINGS)
- The industrial internet of things (IIoT) is a term that refers to interconnected sensors, instruments, and other devices that are networked with industrial applications on computers, such as manufacturing and energy management.
- Data gathering, exchange, and analysis are all possible with this connectivity, which could lead to increased production and efficiency, as well as other economic benefits.
- The IIoT is an evolution of a distributed control system (DCS) that uses cloud computing to enhance and optimize process controls, allowing for a higher degree of automation.
What is IOT architecture ?
IOT systems are typically envisioned as a layered modular digital technology architecture. The physical components, such as CPS, sensors, or machines, are referred to as the device layer. The network layer, which consists of physical network buses, cloud computing, and communication protocols that aggregate and transport data to the service layer, which consists of applications that manipulate and combine data into information that can be displayed on the driver dashboard, is made up of applications that manipulate and combine data into information that can be displayed on the driver dashboard. The content layer, often known as the user interface, is at the top of the stack.

application IOT architecture
The use of IIoT in vehicle manufacturing necessitates the digitalization of all production elements. The interconnectedness of software, robots, and humans allows suppliers and manufacturers to respond quickly to changing standards.
By sending data from customers to the company’s systems, and then to various areas of the manufacturing process, the IIoT enables efficient and cost-effective production.
New tools and capabilities can be incorporated into the production process thanks to the IIoT.
For Example-3D printers, for example, make it easier to shape pressing tools by manufacturing the shape straight from steel granulate. These technologies open up new design possibilities (with high precision).
Because of the versatility and connectivity of the IIoT, vehicle customization is also possible. Humans and robots used to work separately, but the IIoT now allows them to collaborate.
Robots perform heavy and repetitive tasks, resulting in shorter manufacturing cycles and a faster time to market for the car. Factories can immediately identify possible maintenance concerns before they cause downtime, and many are transitioning to a 24 hour manufacturing facility for increased security and efficiency.
The majority of automobile manufacturers have operations in many countries where different components of the same car are manufactured. The IIoT allows these manufacturing plants to communicate with one another, allowing for movement throughout the facilities. Big data can be graphically watched, allowing businesses to respond more quickly to changes in production and demand.
With IIoT support, large amounts of raw data can be stored and sent by the drilling gear and research stations for cloud storage and analysis. With IIoT technologies, the oil and gas industry has the capability to connect machines, devices, sensors, and people through interconnectivity, which can help companies better address fluctuations in demand and pricing, address cyber security, and minimize environmental impact. Across the supply chain, IIoT can improve the maintenance process, the overall safety, and connectivity. Drones can be used to detect possible oil and gas leaks at an early stage and at locations that are difficult to reach
(e.g. offshore). They can also be used to identify weak spots in complex networks of pipelines with built-in thermal imaging systems. Increased connectivity (data integration and communication) can help companies with adjusting the production levels based on real-time data of inventory, storage, distribution pace, and forecasted demand. For example, a Deloitte report states that by implementing an IIoT solution integrating data from multiple internal and external sources (such as work management system, control center, pipeline attributes, risk scores, inline inspection findings, planned assessments, and leak history), thousands of miles of pipes can be monitored in real-time. This allows monitoring of pipeline threats, improving risk management, and providing situational awareness.
Benefits also apply to specific processes of the oil and gas industry. The exploration process of oil and gas can be done more precisely with 4D models built by seismic imaging. These models map fluctuations in oil reserves and gas levels, they strive to point out the exact quantity of resources needed, and they forecast the lifespan of wells. The application of smart sensors and automated drillers gives companies the opportunity to monitor and produce more efficiently. Further, the storing process can also be improved with the implementation of IIoT by collecting and analyzing real-time data to monitor inventory levels and temperature control. IIoT can enhance the transportation process of oil and gas by implementing smart sensors and thermal detectors to give real-time geolocation data and monitor the products for safety reasons. These smart sensors can monitor the refinery processes, and enhance safety. The demand for products can be forecasted more precisely and automatically be communicated to the refineries and production plants to adjust production levels.
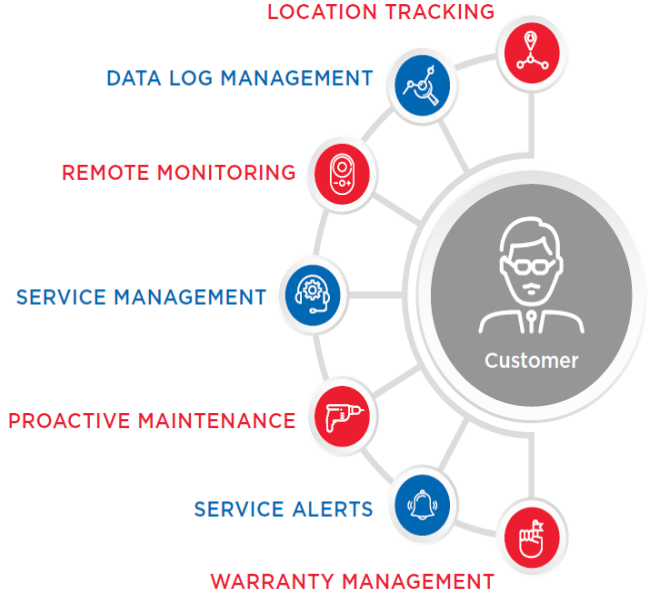
- Real-time Fuel Consumption
- Unscheduled Approval Mechanism leads to loss of productivity efforts
- Zero Visibility towards usage of equipment
- Real-time Working-versus-idle time
- Huge losses on account of Fuel Theft
- Manual Process to Maintain Log Sheet for Fuel Consumption
- Real-time Asset Performance
- Real-time Asset location and Protections
Insights
- Reduce fuel consumption
- Increase equipment life
- Improve productivity
- Improve utilizations
- Compliance cost
- Reduce equipment breakdown
- Proactive maintenance
- Reduce asset cost
Identification
- Underperforming equipment
- Geofencing
- Site wise asset allocation
- Equipment availability
Reports
- Realtime Site Log sheet
- Expense tracking
- Productivity
- Utilization
- Linking of productivity with fuel norms